Email cannot be empty
Password cannot be empty
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent


The structure of the human ear is much more complex than what we see on the surface. The ear can sense and process frequencies ranging from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, approximately the frequency of high octaves. However, the range that the human ear can tolerate is far beyond that. Ear damage is highly prone and irreversible. Personal hearing loss caused by noise sources in the work environment can result in employees demanding huge compensation from employers. While emphasizing hearing protection, excessive protection should also be avoided.
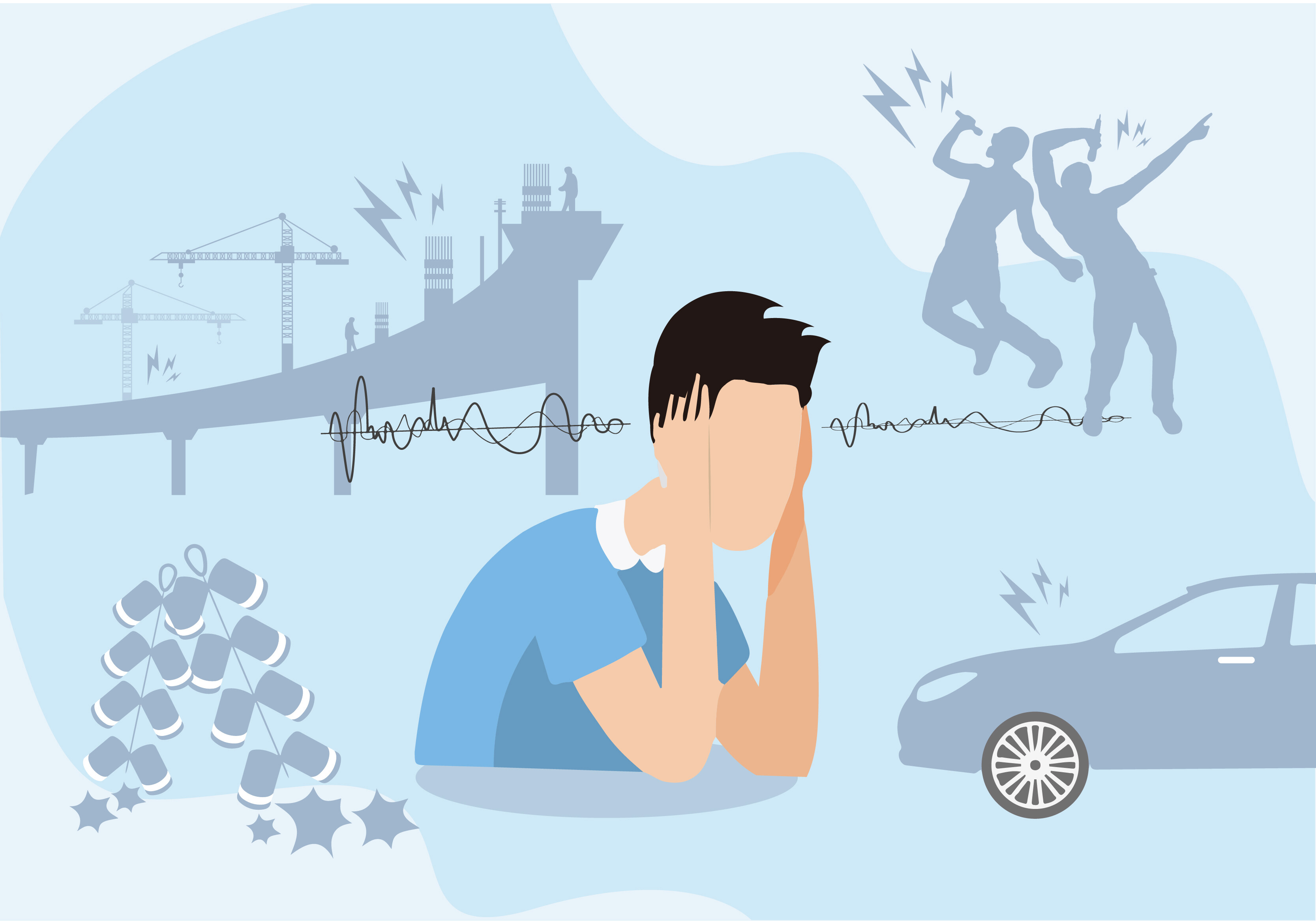

Noise is a sound that makes people uncomfortable, bored, and even unbearable in life and work. It is usually an irregular combination of various frequencies and intensities of sound. The production noise generated in the production environment is also known as industrial noise.
Hazards of noise
Early hearing loss is most likely to occur at 4000Hz and is bilateral symmetric. Patients are mainly unable to hear soft and high-frequency sounds. Unless suddenly exposed to very strong sounds such as gunfire, firecrackers, etc., hearing loss is also gradual.
The impact of noise on the human body is multifaceted. Above 50dB (A) begins to affect sleep and rest, especially in elderly and sick individuals who are more sensitive to noise; Interference of over 70dB (A) in conversation, hindering clear signal listening, causing restlessness, lack of concentration, affecting work efficiency, and even causing accidents; Long term exposure to noise above 90dB (A) can cause hearing loss and occupational deafness, and even affect the normal physiological functions of other systems.
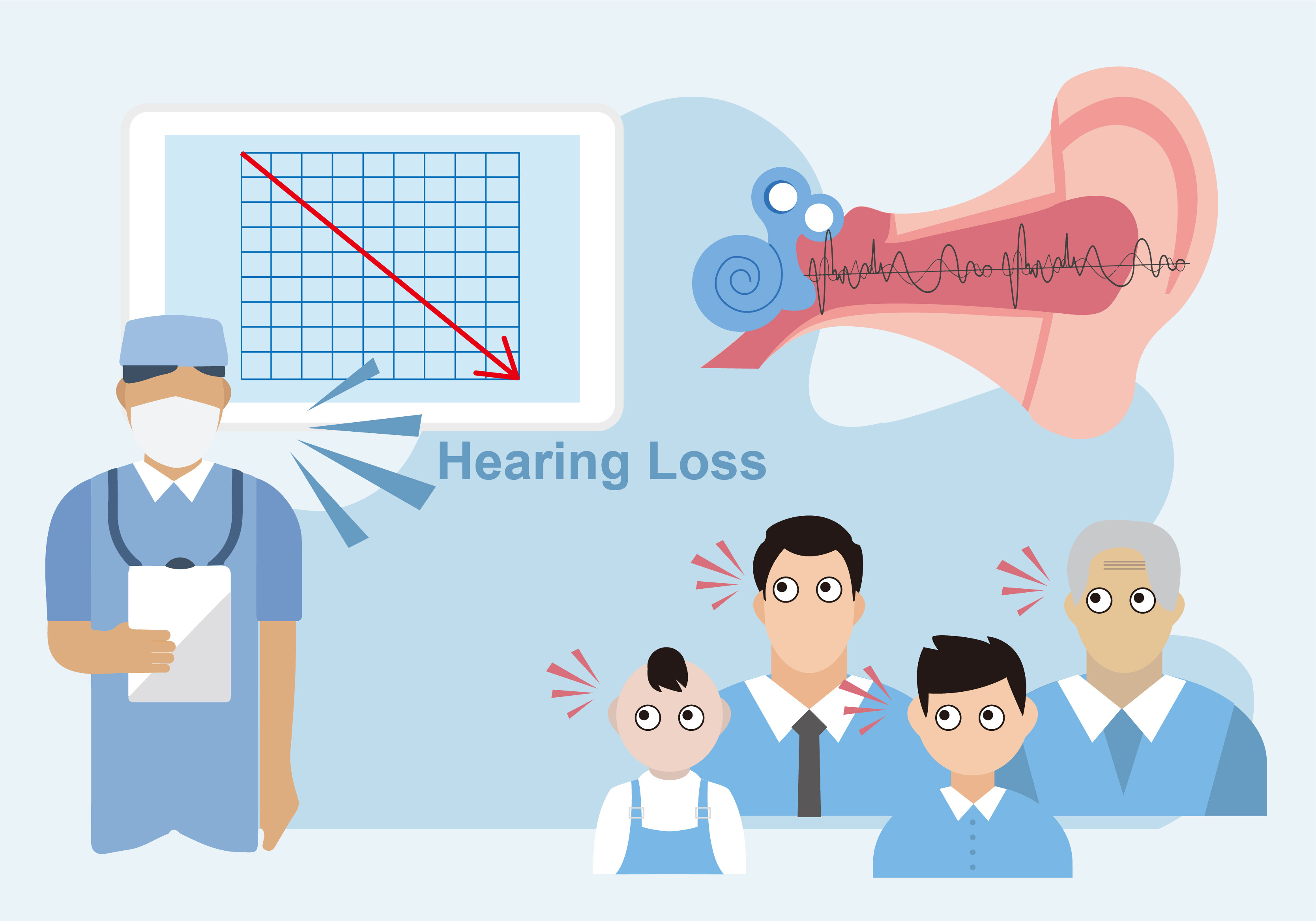
Hearing loss initially refers to a decrease in high-frequency hearing, with no impact on speech frequency, so it does not hinder daily conversations and conversations. Due to improper protection or the lack of necessary protective measures, explosive deafness can cause serious damage to the auditory system due to the strong noise and shock wave generated by the explosion. The patient complained of tinnitus, earache, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. Examination can reveal severe hearing impairment or even complete deafness. If the inner ear is not severely damaged, hearing can be fully or partially restored.
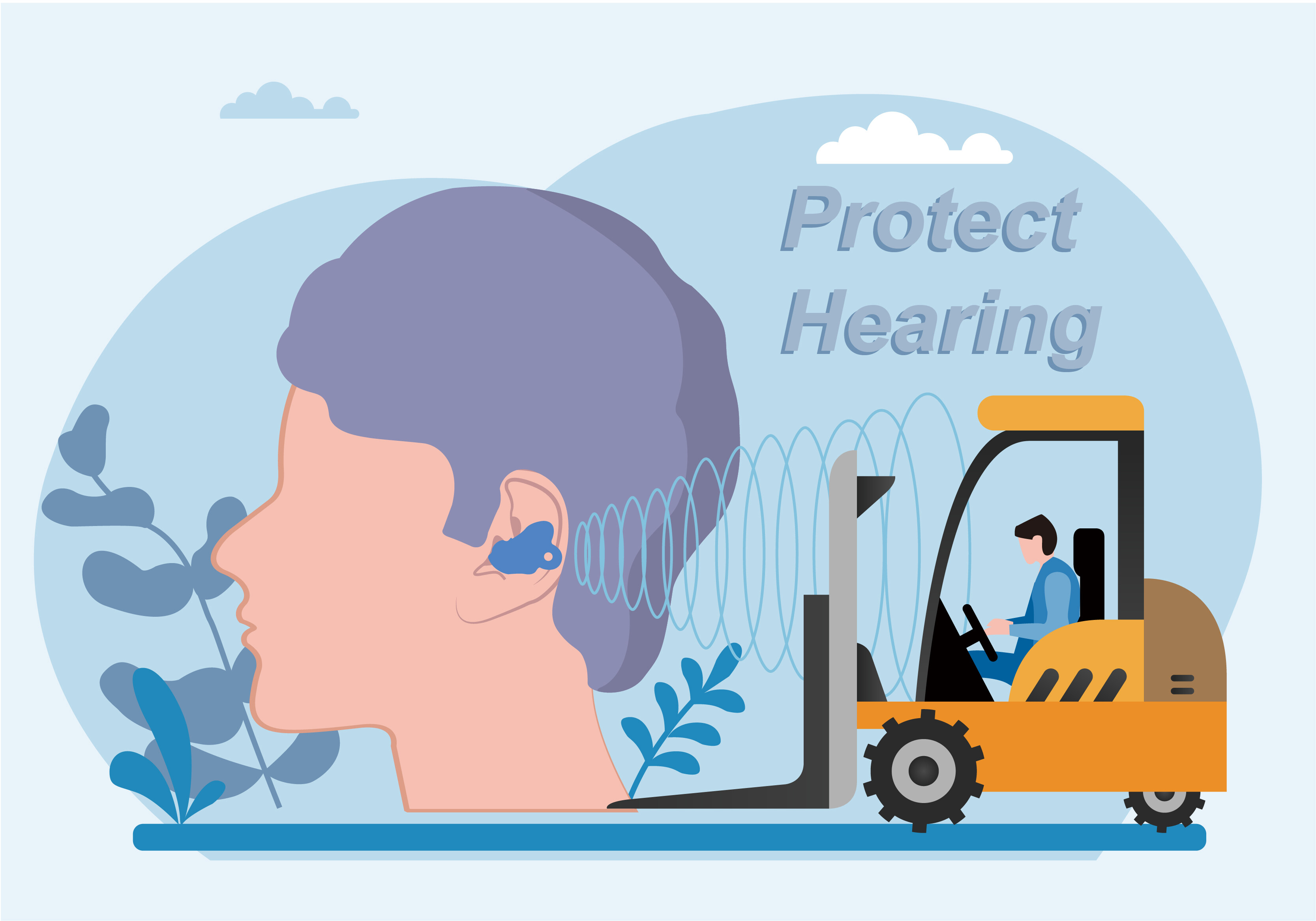
Noise is everywhere, we must do a good job in noise protection and protect our ears. Only with good listening can one fully enjoy life and listen without worries!