Email cannot be empty
Password cannot be empty
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent


After long-term exposure to strong noise, the auditory system will undergo a process from physiological response to pathological change, that is, from auditory adaptation, auditory fatigue to noise induced deafness.
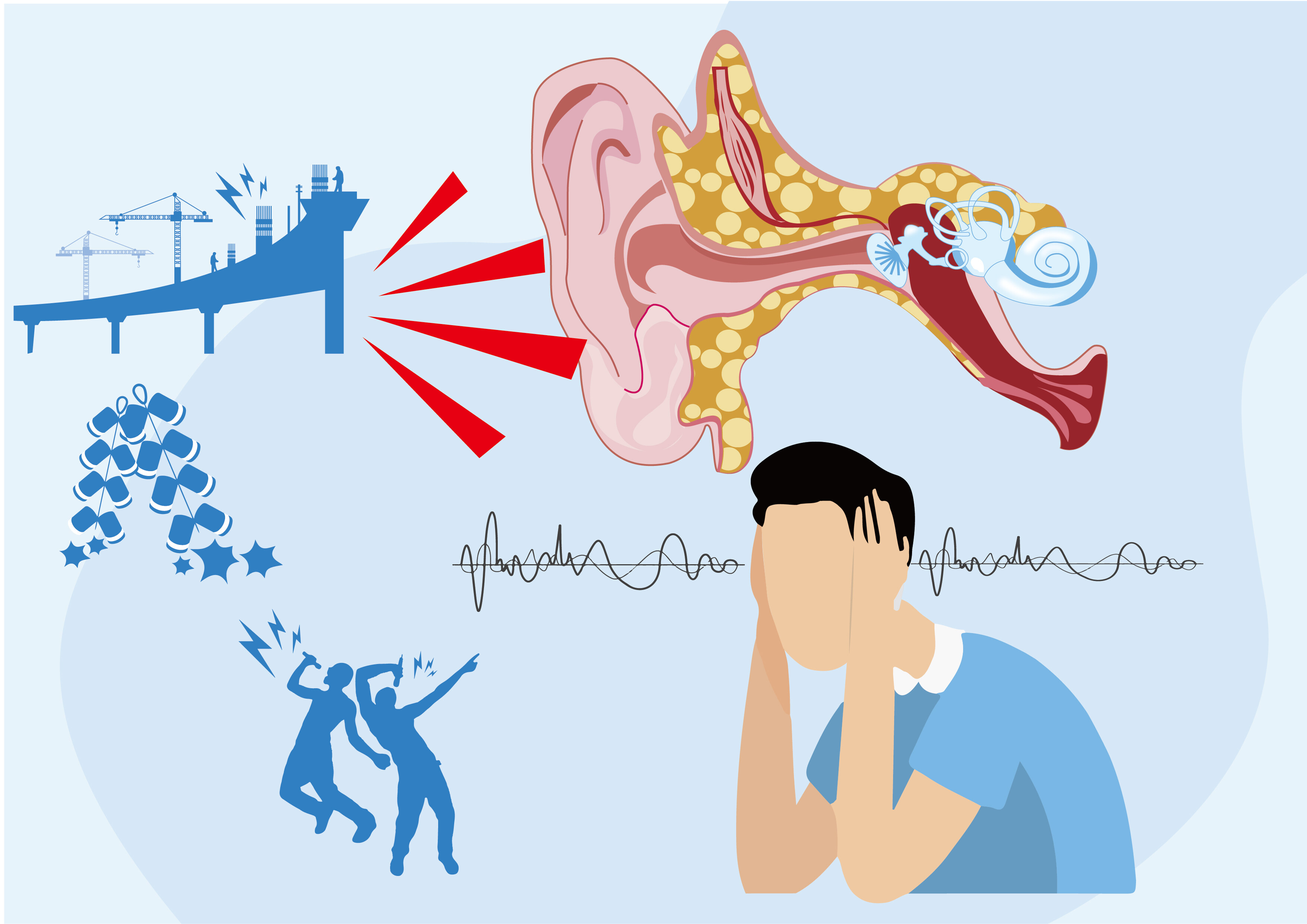
1. Noise induced deafness
On the basis of hearing fatigue, if no protective measures are taken and strong noise is continuously exposed, the sensory organs of the Auditory system will undergo degenerative changes, and the hearing loss cannot be completely recovered, which will become a permanent threshold shift. According to the process of hearing loss, permanent hearing threshold displacement can be further divided into hearing loss and noise induced deafness.
2. Auditory fatigue
There is a certain limit to auditory adaptation. Long term or repeated exposure to a certain level of noise can significantly reduce hearing and increase the hearing threshold by 15 decibels or even more. After leaving the noisy environment, it takes several hours or even more to complete the restoration of normal function, which is a phenomenon of significant changes in the function of the auditory organs called auditory fatigue. Hearing fatigue is a functional change that can be restored, and the length of recovery time varies depending on the intensity and duration of exposure to noise.
3. Auditory adaptation
Short term exposure to noisy environments can result in harsh sounds, discomfort, and tinnitus, leading to a decrease in the sensitivity of the auditory organs. At this point, when hearing is checked, the hearing threshold increases by more than 10 decibels, but after leaving the noisy environment for a few minutes, it quickly returns to normal. This phenomenon is called auditory adaptation. Auditory adaptation is a protective physiological response of the human body.
Hearing loss is an early manifestation of noise induced hearing loss. In its early stages, the patient subjectively has no sense of deafness, but during hearing tests, it is manifested as damage to the high-frequency sound centered around 4000 Hz, with an increase in hearing threshold and a decrease in hearing. The hearing curve is in the range of 3000 to 6000 Hz, with a "V" shaped depression, while the low-frequency range is not affected, which does not hinder conversation. The hearing impaired person mainly complains of dizziness, insomnia, fatigue, and tinnitus.
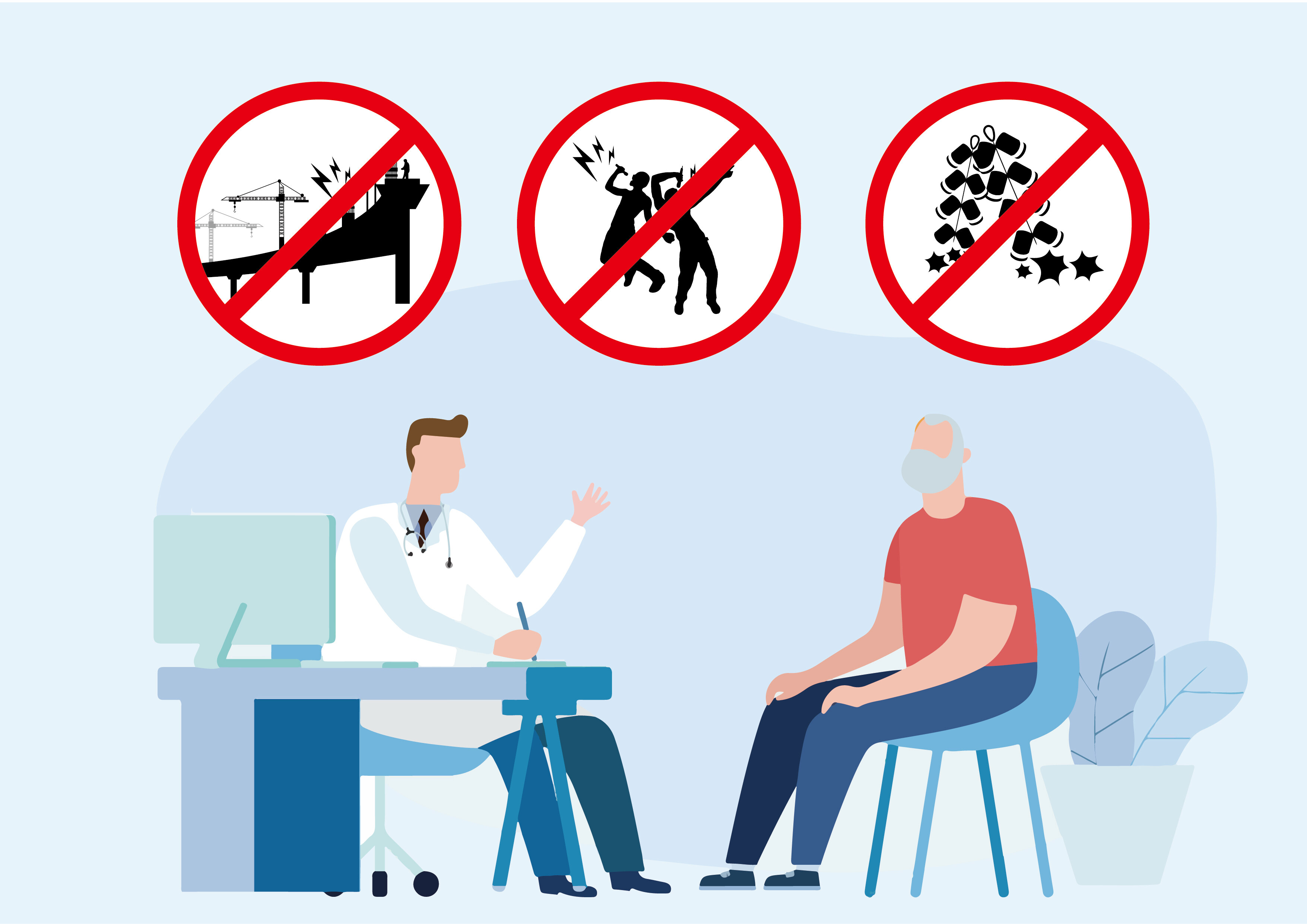

Noise induced hearing loss is a further development of hearing loss. On the basis of a decrease in the high-frequency range, the hearing curve continues to extend towards the low-frequency and high-frequency ends, causing serious damage to language and hearing. Subjective perception of hearing loss results in significant tinnitus in patients. Noise induced hearing loss is an occupational disease, so it is necessary to wear hearing protection equipment such as noise resistant earplugs and earmuffs in daily life.